Since the inception of human kind, humans have been looking for ways to effectively and smartly take decisions. The term business intelligence (BI), which simply putting is using technology for effective decision-making, was coined much later i.e. in mid of last century. In the past two decades, the world of technology has seen myriad of developments. It is interesting to see how those developments have transformed the approach and perspective of technology practitioners and specifically the field of BI. In this article, we are going to discuss the future of BI. We will also analyze what new developments are underway and how they can be effectively utilized in the field of BI and analytics.
Future of BI
Businesses have always struggled with making right decision using the right data and information. Starting in late 1970s, the notion of decision support systems (DSS) was introduced. Morton (1971) is considered the first practitioner to coin the term “decision support system”. Early DSS were usually using basic analysis techniques like decision support systems and statistics. In 1980s, as the computational and storage capacity was increased executive information systems (EIS) were introduced. EIS made use of high level programming languages such as C and C++. Eventually these precursor systems evolved to formulate BI.
Today, we have more computational and storage power available. BI can leverage that power to help decision makers in effective decision-making. New technologies like visual analytics, cloud computing, Big Data, Internet of things (IOT), and artificial intelligence has already started to play a non-trivial role in BI. In future, BI is going to be more real-time in nature and visual in appearance, where somebody interacting with the BI tools will not have to be tech-savvy in order to uncover hidden patterns and insights from the information.
Real-Time Insights
Availability of real time insights is very critical in many industries. Lets consider a scenario where an airline help desk has to respond to a query about most optimal itinerary from point A to point B. The actionable information should entail several features such as weather, flight time and ticket cost. If the insights were not real-time, the help-desk would not be able to effectively answer this question. Thus, real-time insights are paramount. When the technologies like IoT will become more prevalent, we will have more real time streams of data flowing in, and it will be imperative to take those streams in account for actionable insights.
Visual Analytics
Visual analytics is expression of actionable information and insights in form visual graphs and charts. A picture speaks a thousand words, the motivation for visual analytics come from this phrase. The idea is that not every one knows complex programming and SQL queries, which is critical in BI if insights are not available as visual analytics. Therefore, the insights have to be conveyed through visual means.
Dashboards
Dashboards are one of the most popular trends in BI. Dashboards play a pivotal role in the visuals of BI. The visual analytic graphs and charts live in a dashboard. The intent of providing a dashboard is to provide a quick overview of all important metrics and key-performance-indicators (KPIs) using charts and graphs. Dashboards are already very common and in the future, they will become an integral part of any BI setup. Figure 1 depicts an example dashboard.
New Technology Trends and their Application in BI
In this section, we will go over some of the technologies that are being evolved or under development and will analyze how they can be effectively used for BI.
Big Data
The field of BI saw some real traction in first two decades of this century. The latest addition to decision support capabilities was Big Data. Hoffer, Ramesh and Topi (2016) described Big Data as; “Big data has been one of the most frequently covered concepts in the popular business press during the last few years. Even though it is clear that some of the enthusiasm related to big data is overheated, it is equally evident that big data represents something new, interesting, and quite promising.” (p. 447). Big Data is not a single technology rather it is a combination of several tools and techniques such as data warehouses, data and text mining, artificial intelligence and machine learning, service oriented architectures (SOA), application programmer interface (API), cloud computing, and analytics. The idea is to provide unlimited power for BI purposes.
Big Data can be used to process and produce actionable insights for BI at an impressive “velocity”. Big Data can help in storing batch or real time corpus (the raw data) and extract the insights from it while ensuring the data integration and quality is not compromised.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is an evolution of grid computing where a task is processed on a cluster of nodes. The cluster of nodes can be under the same roof or can be geographically dispersed. Small and mid-size businesses can now leverage the power of cloud computing to perform processing that requires very large in-house infrastructures otherwise. Some cloud computing models are SaaS, Iaas, PaaS and BaaS.
BI inherently requires large computational power; with cloud computing businesses only have to pay for what they use (Pay-per-use model). Thus, BI is in reach of small and mid size businesses.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and BI is a natural match. AI is inherently based on the idea of smart agents which given an input used automatic reasoning to figure out the function that will generate the appropriate output (Poole & Mackworth, 2017). While figuring out the function, the smart agent can take the produced outputs in account as well. Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI and it is widely used for classification (prediction and regression) in several industries (Sharda, Delen & Turban, 2014). ML models are constantly being evaluated and retargeted for performance optimization. Data science is tightly coupled with AI to process very large datasets.
AI along with data science is used to make the overall pattern recognition and insight extraction easier for BI. Model optimization part of ML specifically is very useful for BI, because it ensures that decision-making insights are up to date and correct.
Quantum Computing
Next big thing is Quantum Computing, which is a direct application of quantum physics in computer science where small particles such as photons and electrons are used for processing. Quantum computing will increase the speed of computers exponentially. A qubit is a representation of measure at orthogonal axes and forms the basic block of quantum computers.
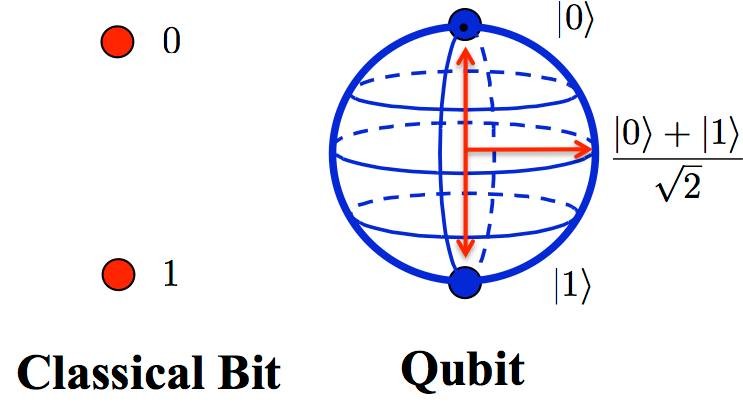
With Quantum computing, the processing power will be drastically improved and “commodity” hardware will be able to perform resource intensive tasks for BI. Quantum computing is still in its infancy phases yet.
Conclusion
We discussed how in future the BI is going to be real-time and visual in appearance and nature so that a less tech savvy stakeholder can get insights for decision-making. Technologies like Big Data, Cloud computing and AI have already started to change how things used to work in BI and have made the BI tools and techniques more effective. Quantum computing is next big thing and it going to drastically increase the processing power available to us today and will definitely have a big positive impact on BI.
References
Morton, S. (1971). Management decision systems: computer-based support for decision making.
Hoffer, J. A., Ramesh, V., & Topi, H. (2016). Modern database management Twelfth Edition. Boston, MA: Pearson Education.
Poole, D. L., & Mackworth, A. K. (2017). Artificial Intelligence (2nd ed.). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Sharda, R., Delen, D. & Turban, E. (2014). Business Intelligence (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.

